A flight averages 460 miles – The average distance covered by a flight stands at 460 miles, offering insights into the intricate dynamics of air travel. This figure serves as a valuable benchmark, shaping our understanding of flight patterns, travel planning, and the impact on various aspects of aviation.
The factors influencing flight distance, such as aircraft size, fuel efficiency, and flight routes, paint a vivid picture of the complexities involved in determining the optimal distance for air travel.
Average Flight Distance
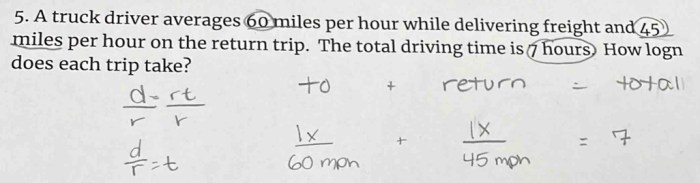
The average flight distance varies depending on the type of aircraft and the flight route. Commercial aircraft typically have a longer average flight distance than private or military aircraft.
Factors that influence the average flight distance include aircraft size, fuel efficiency, and flight route. Larger aircraft can carry more fuel and fly longer distances. More fuel-efficient aircraft can also fly longer distances on the same amount of fuel. And shorter flight routes obviously result in shorter average flight distances.
Commercial Aircraft
The average flight distance for commercial aircraft is around 1,000 miles. However, this can vary significantly depending on the size of the aircraft and the flight route. For example, a small regional jet may have an average flight distance of around 500 miles, while a large wide-body jet may have an average flight distance of around 2,000 miles.
Private Aircraft
The average flight distance for private aircraft is around 500 miles. However, this can also vary significantly depending on the size of the aircraft and the flight route. For example, a small piston-engine aircraft may have an average flight distance of around 200 miles, while a large turboprop aircraft may have an average flight distance of around 1,000 miles.
Military Aircraft
The average flight distance for military aircraft varies widely depending on the type of aircraft and its mission. For example, a fighter jet may have an average flight distance of around 500 miles, while a long-range bomber may have an average flight distance of around 5,000 miles.
Impact on Travel Time: A Flight Averages 460 Miles
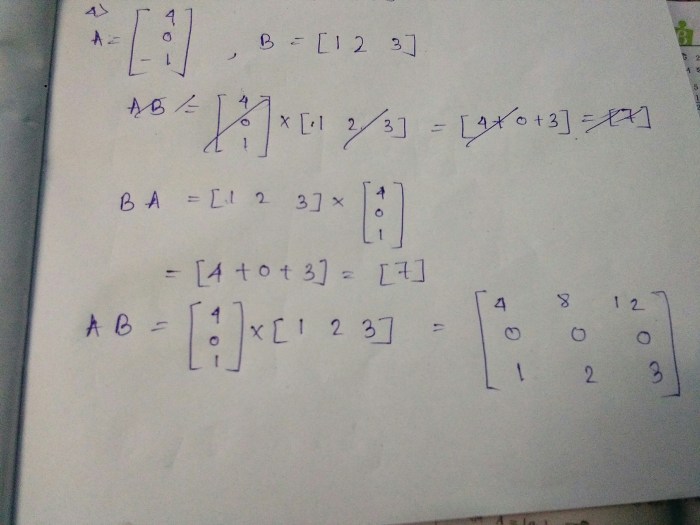
Calculating the travel time for a flight averaging 460 miles involves considering several factors that can affect the aircraft’s speed and altitude. These include wind speed, direction, and altitude, as well as the aircraft’s type and weight.
Generally, aircraft fly at altitudes between 30,000 and 40,000 feet, where the air is less dense and offers less resistance. However, factors like weather conditions and air traffic can impact the chosen altitude.
Wind Speed and Direction
Wind speed and direction can significantly influence flight time. Tailwinds, or winds blowing in the same direction as the aircraft, can reduce travel time, while headwinds, or winds blowing opposite the aircraft’s direction, can increase it.
For instance, if an aircraft flies 460 miles with a tailwind of 20 knots (approximately 23 miles per hour), it will cover the distance in less time compared to flying against a headwind of the same speed.
Fuel Consumption and Emissions

The distance of a flight significantly influences its fuel consumption and environmental impact. This section examines the fuel consumption estimates for flights averaging 460 miles, considering aircraft type and fuel efficiency. Additionally, it analyzes the impact of flight distance on carbon emissions and air pollution.
Fuel Consumption Estimates
Fuel consumption for a flight depends on several factors, including aircraft size, engine efficiency, and flight conditions. For a 460-mile flight, a typical narrow-body aircraft, such as the Boeing 737 or Airbus A320, consumes approximately 1,500-2,000 gallons of jet fuel.
The fuel efficiency of an aircraft is measured in terms of miles per gallon (mpg). Newer aircraft models tend to be more fuel-efficient due to advancements in engine technology and aerodynamic design. For example, the Boeing 787 Dreamliner has an mpg of around 30, while older aircraft like the Boeing 747 have an mpg of around 20.
Environmental Impact
Flight distance directly impacts carbon emissions and air pollution. Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the primary greenhouse gas emitted by aircraft engines, contributing to climate change. Additionally, aircraft emit nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter, which can harm air quality and human health.
A 460-mile flight generates approximately 2-3 tons of CO2 per passenger. The environmental impact increases with longer flight distances. For instance, a transatlantic flight from New York to London emits around 10-15 tons of CO2 per passenger.
Did you know that a flight averages around 460 miles? If you’re curious about the psychological aspects of aviation, be sure to check out unit 9 ap psychology vocab for a comprehensive overview. By understanding the cognitive processes and emotional experiences involved in flying, we can enhance safety and improve the overall passenger experience.
So, the next time you’re soaring through the skies at 460 miles per hour, take a moment to reflect on the fascinating psychological dynamics at play.
Economic Considerations
The relationship between flight distance and ticket pricing is intricate, influenced by a multitude of factors. Fuel costs, a significant operational expense for airlines, play a pivotal role. Longer flights necessitate greater fuel consumption, directly impacting ticket prices.
Flight distance also affects airline profitability. Extended flights incur higher operating expenses, including crew salaries, aircraft maintenance, and airport fees. These costs must be balanced against ticket revenue to ensure profitability. Consequently, airlines often adjust ticket prices based on flight distance to maintain financial viability.
Consumer Affordability
Flight distance can impact consumer affordability. Longer flights typically command higher ticket prices, which may limit accessibility for budget-conscious travelers. This can create disparities in travel opportunities and hinder equitable access to air transportation.
Technological Advancements
The pursuit of extended flight distances has been a driving force behind advancements in aircraft technology. In recent years, significant strides have been made in improving aerodynamics and fuel efficiency, enabling aircraft to travel farther with reduced fuel consumption.
Aerodynamic Enhancements
Modern aircraft designs incorporate advanced aerodynamic features that reduce drag and improve lift. These include winglets, which extend the wingspan and enhance airflow efficiency, and laminar flow control systems that smooth out the airflow over the aircraft’s surface.
Fuel-Efficient Engines
Significant progress has been made in developing more fuel-efficient engines for aircraft. Turbofan engines, which use a combination of a fan and compressor, have become the industry standard due to their improved fuel economy. Additionally, hybrid-electric propulsion systems are being explored to further reduce fuel consumption.
Future Innovations
Research and development efforts continue to push the boundaries of aircraft technology. Future innovations that could further extend flight distance include:
- Advanced materials that reduce aircraft weight and improve structural integrity
- Adaptive wing designs that optimize aerodynamic performance for different flight conditions
- Electric and hydrogen-powered propulsion systems that offer zero or low emissions
Geographic Implications
Flight distance limitations have significant geographic implications, affecting regions and countries differently. Understanding these implications is crucial for planning, infrastructure development, and economic growth.
Regions with vast distances, such as island nations or remote areas, face challenges in accessibility and connectivity. Limited flight distances restrict the movement of people and goods, hindering economic development and social progress.
Impact on Accessibility
Flight distance limitations impact accessibility in several ways:
- Limited flight routes and frequencies make it challenging to reach remote destinations.
- Long flight times increase travel time and reduce the convenience of air travel.
- High ticket prices associated with long-distance flights can limit affordability for many travelers.
Passenger Experience
Long-distance flights can impact passenger comfort and convenience in several ways. Passengers may experience fatigue, discomfort, and boredom during extended periods in the air. Airlines have implemented strategies to enhance the passenger experience during long-distance flights, such as providing in-flight entertainment and amenities.
In-flight Entertainment and Amenities, A flight averages 460 miles
Airlines offer various forms of in-flight entertainment to keep passengers engaged during long flights. These include movies, TV shows, music, and games. Some airlines also provide Wi-Fi connectivity, allowing passengers to stay connected with work, family, and friends. Additionally, airlines provide amenities such as comfortable seats, blankets, and pillows to enhance passenger comfort.
Q&A
What factors affect the average flight distance?
Aircraft size, fuel efficiency, and flight routes are key factors that influence the average flight distance.
How does flight distance impact travel time?
Flight distance directly affects travel time, with longer distances resulting in increased travel time, considering factors like wind speed and altitude.
What are the economic implications of flight distance?
Flight distance influences ticket pricing, fuel costs, and operating expenses, impacting airline profitability and consumer affordability.