Is eubacteria multicellular or unicellular – Delving into the intriguing world of microbiology, we explore the fundamental question: are eubacteria multicellular or unicellular? Embark on a captivating journey as we unravel the intricacies of these diverse microorganisms, their structural complexities, and ecological significance.
Eubacteria, a vast and ubiquitous group of prokaryotes, exhibit a remarkable range of cellular organizations. From the simplicity of unicellular forms to the complexity of multicellular arrangements, their cellular structures and functions hold profound implications for their ecological roles and evolutionary origins.
Definition of Multicellular and Unicellular
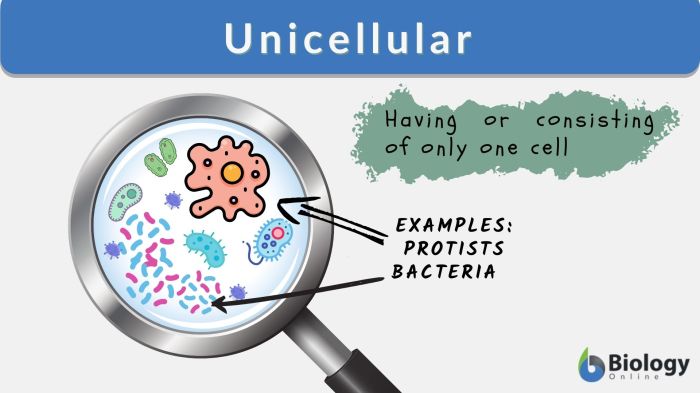
Multicellular organisms are composed of multiple cells that are specialized for different functions. They exhibit a high level of organization and coordination, with cells working together to form tissues, organs, and organ systems.Unicellular organisms, on the other hand, consist of a single cell that performs all the necessary functions for life.
They are typically smaller and less complex than multicellular organisms, but they can still exhibit remarkable adaptations and play vital roles in various ecosystems.
Eubacteria Classification: Is Eubacteria Multicellular Or Unicellular
Eubacteria, also known as true bacteria, are classified under the domain Bacteria. They are further divided into several phyla, including:
- Proteobacteria
- Firmicutes
- Bacteroidetes
- Actinobacteria
- Cyanobacteria
Each phylum contains various subgroups, with specific characteristics and ecological roles.
Structural Organization of Eubacteria
Eubacteria exhibit a diverse range of sizes, shapes, and complexity. Some bacteria are spherical (cocci), rod-shaped (bacilli), or spiral (spirilla). They lack membrane-bound organelles, but they do have specialized structures such as ribosomes, plasmids, and flagella.
Cellular Complexity
Compared to eukaryotes, Eubacteria have a relatively simple cellular organization. They lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, which means that their genetic material is located directly in the cytoplasm. However, some Eubacteria do have specialized structures, such as magnetosomes, which allow them to orient themselves in response to magnetic fields.
Examples of Multicellular and Unicellular Eubacteria
Multicellular Eubacteria are rare, but they do exist. One example is Myxococcus xanthus, which forms fruiting bodies when starved for nutrients. Unicellular Eubacteria are far more common and include a wide range of species, such as:
- Escherichia coli (intestinal bacteria)
- Bacillus subtilis (soil bacteria)
- Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumonia-causing bacteria)
Ecological Significance
Eubacteria play crucial roles in various ecosystems. Multicellular Eubacteria, such as Myxococcus xanthus, contribute to nutrient cycling by decomposing organic matter. Unicellular Eubacteria have diverse roles, including:
- Nitrogen fixation
- Decomposition
- Symbiotic relationships
Evolutionary Implications
The multicellular or unicellular nature of Eubacteria has significant evolutionary implications. Multicellularity is thought to have evolved as a way to increase size and complexity, while unicellularity allows for rapid reproduction and adaptation to changing environments. The presence or absence of specialized structures and organelles in Eubacteria provides insights into the evolutionary history and potential origins of different cellular organizations.
Popular Questions
What is the defining characteristic of multicellular organisms?
Multicellular organisms are characterized by the presence of multiple cells that are organized into tissues and organs, allowing for complex functions and specialization.
How do unicellular organisms differ from multicellular organisms?
Unicellular organisms are self-contained entities consisting of a single cell that performs all necessary functions for survival and reproduction.
What are the different subgroups within Eubacteria?
Eubacteria are classified into various subgroups based on their metabolic capabilities, cell wall structure, and other characteristics, including Gram-positive bacteria, Gram-negative bacteria, and Cyanobacteria.