Where would you least expect to find an ionization nebula? Ionization nebulae are typically associated with regions of active star formation, but recent observations have revealed their presence in unexpected locations, challenging our understanding of their formation and evolution.
This article delves into the intriguing world of ionization nebulae, exploring their unexpected locations, formation processes, and their role in the cosmos.
1. Least Expected Locations for Ionization Nebulae
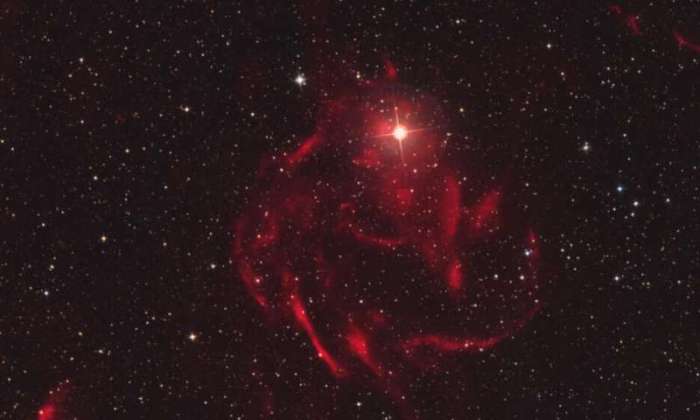

Ionization nebulae are typically associated with regions of active star formation, where the intense radiation from young, hot stars ionizes the surrounding gas. However, ionization nebulae have also been observed in unexpected locations, such as:
- Elliptical galaxies:Elliptical galaxies are typically dominated by old stars and have low rates of star formation. However, some elliptical galaxies have been found to contain ionization nebulae, suggesting that star formation may be occurring in these galaxies after all.
- Quasars:Quasars are extremely luminous active galactic nuclei that are powered by the accretion of matter onto a supermassive black hole. Ionization nebulae have been observed around some quasars, suggesting that the intense radiation from the quasar is ionizing the surrounding gas.
- Planetary nebulae:Planetary nebulae are the shells of gas that are ejected by dying stars. Ionization nebulae have been observed around some planetary nebulae, suggesting that the central star is still emitting enough radiation to ionize the surrounding gas.
2. Formation and Properties of Ionization Nebulae: Where Would You Least Expect To Find An Ionization Nebula
Ionization nebulae are formed when the intense radiation from young, hot stars ionizes the surrounding gas. The process of ionization involves removing electrons from atoms, leaving behind positively charged ions. The ionized gas then emits light at specific wavelengths, which can be observed by astronomers.
The physical properties of ionization nebulae vary depending on the ionizing star and the surrounding environment. However, ionization nebulae typically have temperatures of a few thousand degrees Kelvin, densities of a few hundred particles per cubic centimeter, and are composed of a mixture of hydrogen, helium, and other elements.
3. Role of Ionization Nebulae in Star Formation
Ionization nebulae play an important role in the formation of new stars. The intense radiation from the ionizing star can heat and compress the surrounding gas, triggering the collapse of the gas into stars. Ionization nebulae also provide a reservoir of ionized gas that can be used to form new stars.
The rate of star formation in a region is regulated by the number of ionizing stars and the density of the surrounding gas. In regions with a high density of ionizing stars, the rate of star formation can be very high.
In regions with a low density of ionizing stars, the rate of star formation can be very low.
4. Observational Techniques for Ionization Nebulae
Ionization nebulae can be observed using a variety of observational techniques, including:
- Optical telescopes:Optical telescopes can be used to observe the light emitted by ionization nebulae. This light can be used to determine the temperature, density, and chemical composition of the nebula.
- Radio telescopes:Radio telescopes can be used to observe the radio emission from ionization nebulae. This emission can be used to determine the magnetic field strength and the velocity of the gas in the nebula.
- X-ray telescopes:X-ray telescopes can be used to observe the X-ray emission from ionization nebulae. This emission can be used to determine the temperature of the gas in the nebula.
These observational techniques provide astronomers with a wealth of information about the properties and evolution of ionization nebulae.
5. Scientific Importance of Ionization Nebulae
Ionization nebulae are important objects of study for astronomers because they provide information about the early universe and the formation and evolution of galaxies.
Ionization nebulae are thought to be the sites of the first stars and galaxies. By studying ionization nebulae, astronomers can learn about the conditions in the early universe and how the first stars and galaxies formed.
Ionization nebulae are also important for understanding the formation and evolution of galaxies. Ionization nebulae are often found in the spiral arms of galaxies, where star formation is occurring. By studying ionization nebulae, astronomers can learn about the rate of star formation in galaxies and how it varies over time.
Commonly Asked Questions
What are ionization nebulae?
Ionization nebulae are clouds of ionized gas that emit light due to the presence of high-energy radiation from nearby stars.
Why are ionization nebulae typically found in regions of active star formation?
Active star formation regions provide the intense radiation necessary to ionize the gas in nebulae.
What are some unexpected locations where ionization nebulae have been observed?
Ionization nebulae have been observed in the halos of galaxies, far from any known star formation activity.