As a small drop of water is suspended motionless in air, it invites scientific inquiry and unveils the captivating interplay of physical properties, air resistance, evaporation, and optical effects. This captivating phenomenon, meticulously examined in this discourse, offers a glimpse into the remarkable intricacies of the natural world.
Delving into the unique physical properties of water, we discover the role of surface tension and cohesion in maintaining the spherical shape of the water drop. Air resistance and drag, acting upon the suspended droplet, influence its motion, as quantified by the drag force equation.
Evaporation and condensation, dynamic processes influenced by temperature and humidity, impact the size and shape of the water drop over time.
Physical Properties of Water

Water possesses unique physical properties that enable a small drop to remain suspended motionless in air. Its high surface tension and cohesion play crucial roles in maintaining the shape and stability of the water drop.
Surface tension arises from the strong intermolecular forces between water molecules at the interface between the water drop and the surrounding air. This creates a thin, elastic membrane that acts like a skin, resisting deformation and maintaining the drop’s spherical shape.
Cohesion, on the other hand, refers to the attraction between water molecules within the drop. These cohesive forces hold the molecules together, preventing the drop from disintegrating.
Air Resistance and Drag
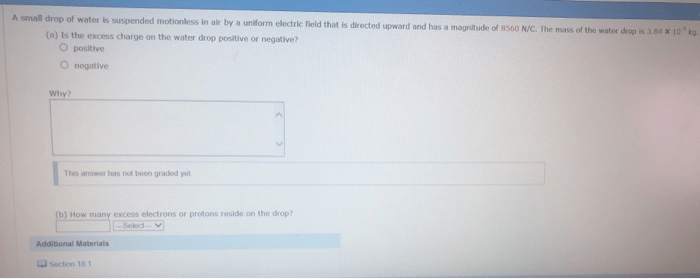
When a water drop is suspended in air, it experiences several forces, including air resistance and drag. Air resistance is the frictional force exerted by the surrounding air on the drop’s surface, opposing its motion.
Drag force is proportional to the drop’s velocity and cross-sectional area. The following equation quantifies the drag force:
$$F_d = \frac12 \rho v^2 A C_d$$
where:
- $$F_d$$ is the drag force
- $$\rho$$ is the air density
- $$v$$ is the drop’s velocity
- $$A$$ is the drop’s cross-sectional area
- $$C_d$$ is the drag coefficient
Evaporation and Condensation
Evaporation and condensation are ongoing processes that affect the size and shape of a suspended water drop. Evaporation occurs when water molecules at the drop’s surface escape into the surrounding air, reducing the drop’s mass and volume.
Conversely, condensation occurs when water vapor in the air condenses onto the drop’s surface, increasing its mass and volume. The rate of evaporation and condensation is influenced by the surrounding temperature and humidity.
At higher temperatures, evaporation is more rapid, while at lower temperatures, condensation dominates.
Optical Effects: A Small Drop Of Water Is Suspended Motionless In Air

Suspended water drops exhibit fascinating optical effects due to their interaction with light. The shape and size of the drop determine its optical properties.
When sunlight strikes a water drop, it undergoes refraction, reflection, and scattering. These interactions produce a spectrum of colors and patterns, including rainbows, halos, and coronas.
Rainbows are formed when sunlight is refracted and reflected within a water drop, creating a circular arc of colors. Halos, on the other hand, are caused by the diffraction of sunlight around the edges of a water drop, producing a bright ring of light around the sun or moon.
Applications and Examples

The suspension of small water drops in air has numerous applications and examples in various fields:
- Inkjet printing:Inkjet printers use tiny drops of ink suspended in air to create precise images and text on paper.
- Cloud formation:Clouds are composed of suspended water drops or ice crystals, which scatter and reflect sunlight, giving them their characteristic appearance.
- Fog harvesting:Fog harvesters collect water from suspended water drops in the air, providing a source of water in arid regions.
- Electrospray ionization:Electrospray ionization is a technique used in mass spectrometry to generate ions from analytes suspended in a liquid droplet.
FAQ Compilation
How does surface tension contribute to the suspension of a water drop?
Surface tension acts as an invisible membrane around the water drop, creating an inward force that counteracts the weight of the water, keeping it suspended.
What factors affect the rate of evaporation of a suspended water drop?
Temperature, humidity, and air movement influence the rate of evaporation, with higher temperatures and lower humidity leading to faster evaporation.
How does the shape of a water drop affect its optical properties?
The spherical shape of a water drop acts as a lens, refracting and reflecting light to create optical phenomena such as rainbows and halos.