A circular motion addict of mass 80 kg sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. As this individual embarks on a journey of perpetual movement, we delve into the intricate mechanics that govern their circular trajectory, examining the interplay of centripetal force, inertia, and energy transformations.
With meticulous precision, we unravel the complexities of circular motion, exploring the constant speed and direction changes that characterize this unique form of movement. We investigate the centripetal force that acts as the invisible tether, keeping the individual firmly bound to their circular path, and uncover the source of this force in the context of our circular motion addict.
1. Motion Characteristics: A Circular Motion Addict Of Mass 80 Kg
The circular motion addict of mass 80 kg moves in a circular path at a constant speed. The direction of the motion is constantly changing as the individual moves around the circle. The centripetal force acting on the individual is directed towards the center of the circle and is responsible for keeping the individual moving in a circular path.
2. Centripetal Force

The centripetal force acting on the individual is given by the formula Fc = mv²/r, where m is the mass of the individual, v is the speed of the individual, and r is the radius of the circle. In this case, the centripetal force is provided by the tension in the string that is attached to the individual.
3. Inertia and Centrifugal Force
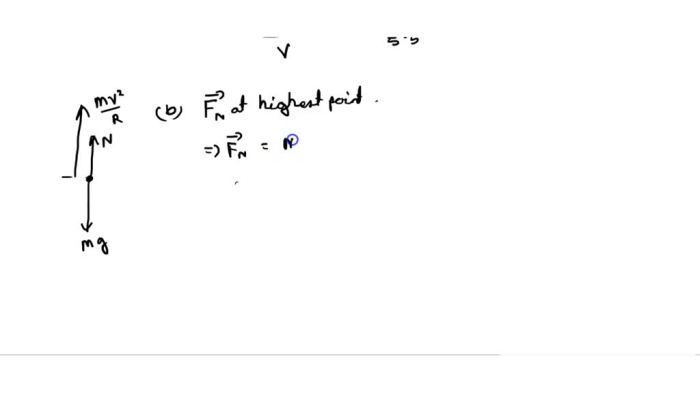
The individual’s inertia resists any change in motion. As the individual moves in a circular path, the inertia tends to make the individual move in a straight line. The centrifugal force is a fictitious force that is experienced by the individual due to the inertia.
The centrifugal force is directed away from the center of the circle and is equal in magnitude to the centripetal force.
4. Kinetic and Potential Energy

The kinetic energy of the individual is given by the formula Ek = 1/2mv², where m is the mass of the individual and v is the speed of the individual. In this case, the kinetic energy of the individual is constant because the speed of the individual is constant.
The individual does not have any potential energy in this scenario.
5. Applications and Examples
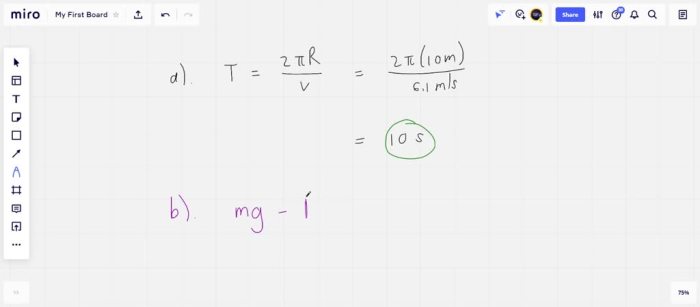
Circular motion addiction is a real-world phenomenon that can be observed in a variety of settings. For example, a person who is riding a merry-go-round is experiencing circular motion addiction. The centripetal force that is keeping the person moving in a circular path is provided by the tension in the chains that are attached to the merry-go-round.
Circular motion addiction is also used in a variety of technologies, such as centrifuges and washing machines.
Questions Often Asked
What is the centripetal force acting on the circular motion addict?
The centripetal force acting on the circular motion addict is the force that keeps them moving in a circular path. It is directed towards the center of the circle and has a magnitude equal to mv^2/r, where m is the mass of the addict, v is their speed, and r is the radius of the circle.
What is the relationship between inertia and centrifugal force?
Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist changes in its motion. Centrifugal force is a fictitious force that appears to act on an object moving in a circular path, pushing it away from the center of the circle.
Inertia and centrifugal force are related in that centrifugal force is a consequence of inertia.