Complete dominance Mendelian genetics worksheet answer key unlocks the mysteries of heredity, providing a comprehensive guide to understanding the fundamental principles of Mendelian genetics. This key unravels the intricacies of complete dominance, shedding light on the fascinating world of inheritance patterns.
Delving into the concepts of homozygous and heterozygous alleles, genotype and phenotype, this answer key empowers readers with the knowledge to decipher the genetic code that governs the traits we inherit.
Complete Dominance in Mendelian Genetics
In Mendelian genetics, complete dominance refers to a situation where one allele of a gene masks the expression of the other allele when both are present in an individual. The dominant allele is the one that is expressed in the phenotype, while the recessive allele is the one that is masked.
Alleles are different forms of a gene that occupy the same locus on homologous chromosomes. Individuals who have two identical alleles for a particular gene are said to be homozygous for that gene. Individuals who have two different alleles for a particular gene are said to be heterozygous for that gene.
The genotype of an individual refers to the genetic makeup of the individual, while the phenotype refers to the observable characteristics of the individual. Complete dominance is important because it affects the phenotype of an individual. If one allele is dominant over another, the phenotype of the individual will be determined by the dominant allele, even if the individual is heterozygous for the gene.
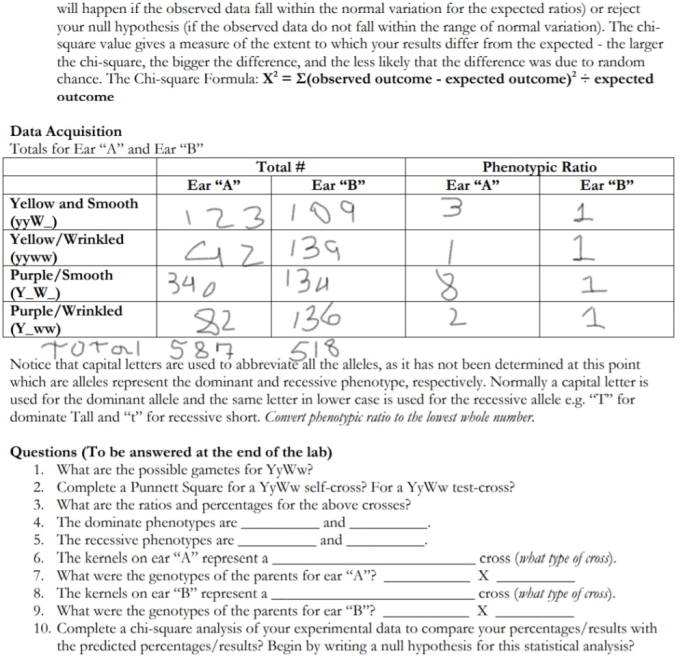
Punnett Squares and Complete Dominance: Complete Dominance Mendelian Genetics Worksheet Answer Key
Punnett squares are used to predict the inheritance patterns of genes. A Punnett square is a diagram that shows the possible combinations of alleles that can be inherited from two parents. In a Punnett square, the alleles of one parent are listed along the top of the square, and the alleles of the other parent are listed along the side of the square.
The squares in the Punnett square represent the possible genotypes of the offspring.
Complete dominance is represented in Punnett squares by the fact that the dominant allele is always expressed in the phenotype of the offspring, regardless of whether the offspring is homozygous or heterozygous for the gene. For example, if one parent has two dominant alleles for a particular gene and the other parent has two recessive alleles for the same gene, all of the offspring will have the dominant phenotype.
Here is an example of a Punnett square that shows the inheritance of a gene for eye color. The dominant allele for brown eyes is B, and the recessive allele for blue eyes is b. If one parent has the genotype BB and the other parent has the genotype bb, all of the offspring will have the genotype Bb and the brown eye phenotype.
Genotype and Phenotype Ratios, Complete dominance mendelian genetics worksheet answer key
The genotype ratio refers to the proportion of different genotypes in a population. The phenotype ratio refers to the proportion of different phenotypes in a population.
For complete dominance, the genotype ratio is 1:2: 1. This means that for every homozygous dominant individual, there will be two heterozygous individuals and one homozygous recessive individual. The phenotype ratio is 3:1. This means that for every three individuals with the dominant phenotype, there will be one individual with the recessive phenotype.
The genotype and phenotype ratios can be used to predict the inheritance patterns of genes. For example, if you know the genotype ratio of a population, you can predict the phenotype ratio of the population.
Examples of Complete Dominance
There are many examples of complete dominance in Mendelian genetics. Some of the most common examples include:
- Eye color
- Hair color
- Blood type
- Height
- Weight
In each of these cases, the dominant allele is responsible for the most common phenotype. For example, the dominant allele for brown eyes is more common than the recessive allele for blue eyes. This means that most people have brown eyes.
Applications of Complete Dominance
Complete dominance is used in a variety of applications, including genetic engineering and breeding programs. In genetic engineering, complete dominance can be used to create organisms with desired traits. For example, scientists have used complete dominance to create genetically modified crops that are resistant to pests and diseases.
In breeding programs, complete dominance can be used to select for desired traits. For example, breeders can use complete dominance to select for animals that have desirable traits, such as increased milk production or meat quality.
Clarifying Questions
What is complete dominance in Mendelian genetics?
Complete dominance occurs when one allele of a gene masks the expression of another allele, resulting in a single phenotype for heterozygous individuals.
How are Punnett squares used to predict inheritance patterns?
Punnett squares are graphical representations that predict the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring based on the genotypes of their parents.
What is the significance of genotype and phenotype ratios?
Genotype and phenotype ratios provide valuable insights into the genetic makeup of a population and the expression of traits within that population.
